완전 탐색 알고리즘 (DFS & BFS)
배열이나 그래프 또는 트리를 탐색하고자 할 때 재귀함수나 큐를 이용한다. 재귀함수를 이용한 탐색 방법을 깊이 우선 탐색(DFS)라고 하고, 큐를 이용한 탐색 방법을 너비 우선 탐색(BFS)라고 한다. 배열과 트리 탐색에 관한 상황에 대해서 DFS와 BFS를 간단하게 구현해보고 차이점을 알아보자.
- N x N구조를 가진 2차원 배열에서 1의 총 개수를 출력
5
1 0 1 0 0
1 1 1 0 0
0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 1
0 0 0 1 0
입력 코드
public class Main {
static int N, answer;
// 배열의 값을 저장할 용도
static int[][] arr;
// 이미 방문한 곳은 더 이상 방문하지 않기 위해 boolean 배열 사용
static boolean[][] check;
static int[] dr = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
static int[] dc = {0, 1, 0, -1};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st;
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
arr = new int[N][N];
check = new boolean[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine(), " ");
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
arr[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
}
}
- 트리 탐색
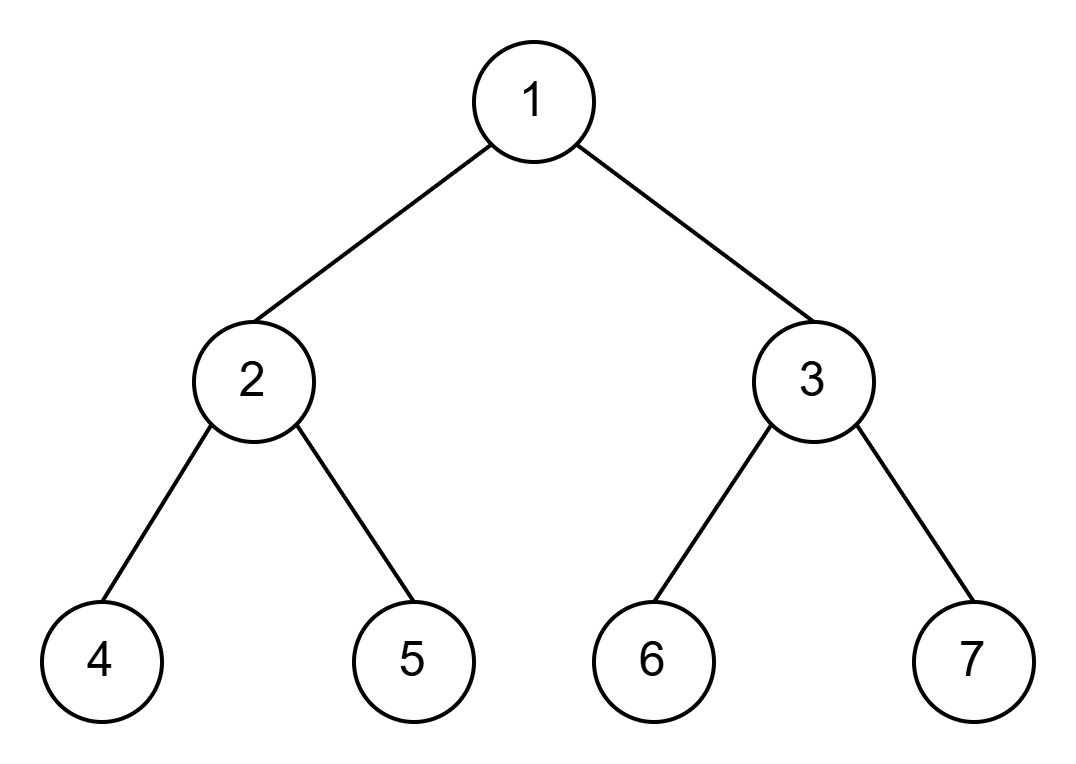
7
6
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
3 6
3 7
입력 코드
public class Main {
static Node[] tree;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st;
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int E = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
tree = new Node[N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine(), " ");
int from = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int to = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
tree[from] = new Node(to, tree[from]);
}
}
}
class Node {
int to;
Node next;
public Node(int to, Node next) {
this.to = to;
this.next = next;
}
}
DFS
탐색이 가능한 곳까지 탐색을 하고, 더 이상 탐색이 불가능하면 탐색이 다시 가능한 분기까지 복귀하여 재탐색한다는 것을 의미한다. 따라서 일반적으로 재귀호출을 이용하여 구현을 한다.
배열 탐색
입력은 위의 입력 코드를 참고하자.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (arr[i][j] == 1 && !check[i][j]) {
dfs(new int[] {i, j});
}
}
}
System.out.println(answer);
}
static void dfs(int[] pos) {
answer++;
check[pos[0]][pos[1]] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nr = pos[0] + dr[i];
int nc = pos[0] + dc[i];
// 범위를 벗어났음을 확인
if (nr < 0 || nc < 0 || nr >= N || nc >= N) continue;
if (check[nr][nc] || arr[nr][nc] != 1) continue;
dfs(new int[] {nr, nc});
}
}
}
트리 탐색
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
dfs(1);
}
static void dfs(int cur) {
for (Node node = tree[cur]; node != null; node = node.next) {
dfs(node.to);
}
}
순회 구현
DFS를 이용하면 순회 구현을 편리하게 할 수 있다. 이때는 연결 리스트 그래프가 아닌 인접 리스트나 인접 행렬을 이용하면 구현하기 쉽다. 코드를 통해 전위순회, 중위순회, 후위순회를 구현해보자.
public class Main {
static List<Integer>[] tree;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st;
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int E = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
tree = new List[N + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) tree[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine(), " ");
int from = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int to = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
tree[from].add(to);
}
dfs(1);
}
static void dfs(int cur) {
// 전위 순회 (현재 노드 방문 → 왼쪽 자식 방문 → 오른쪽 자식 방문)
System.out.print(cur + " ");
for (int next : tree[cur]) {
dfs(next);
}
// 후위 순회 (왼쪽 자식 방문 → 오른쪽 자식 방문 → 현재 노드 방문)
// System.out.print(cur + " ");
}
}
중위 순회는 왼쪽 하위 노드를 방문하고, 현재 노드를 방문한 다음에 오른쪽 하위 노드를 방문해야 하므로 추가적인 코드 작성이 필요하다.
// 중위 순회 (왼쪽 자식 방문 → 현재 노드 방문 → 오른쪽 자식 방문)
static void dfs(int cur) {
if (cur == 0) return;
List<Integer> children = tree[cur];
int mid = children.size() / 2; // 중간 인덱스 계산
// 왼쪽 절반의 자식 방문
for (int i = 0; i < mid; i++) {
dfs(children.get(i));
}
// 현재 노드 방문
System.out.print(cur + " ");
// 오른쪽 절반의 자식 방문
for (int i = mid; i < children.size(); i++) {
dfs(children.get(i));
}
}
BFS
현재 위치에서 모든 것을 탐색할 수 있는 모든 곳을 탐색해나가며 점점 넓혀가는 방식이다.
배열 탐색
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (arr[i][j] == 1 && !check[i][j]) {
bfs(new int[] {i, j});
}
}
}
System.out.println(answer);
}
static void bfs(int[] pos) {
Queue<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(pos);
// 큐에 요소가 없을 때 까지 반복
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
answer++;
int[] cur = queue.poll();
check[cur[0]][cur[1]] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nr = cur[0] + dr[i];
int nc = cur[1] + dc[i];
if (nr < 0 || nc < 0 || nr >= N || nc >= N) continue;
if (check[nr][nc] || arr[nr][nc] != 1) continue;
queue.offer(new int[] {nr, nc});
}
}
}
}
트리 탐색
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
bfs(1);
}
static void bfs(int start) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(start);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int cur = queue.poll();
for (Node node = tree[cur]; node != null; node = node.next) {
queue.offer(node.to);
}
}
}
DFS vs BFS
그렇다면 DFS와 BFS의 차이는 정확하게 어떤 것이 있을까? 우선 표를 통해 살펴보자.
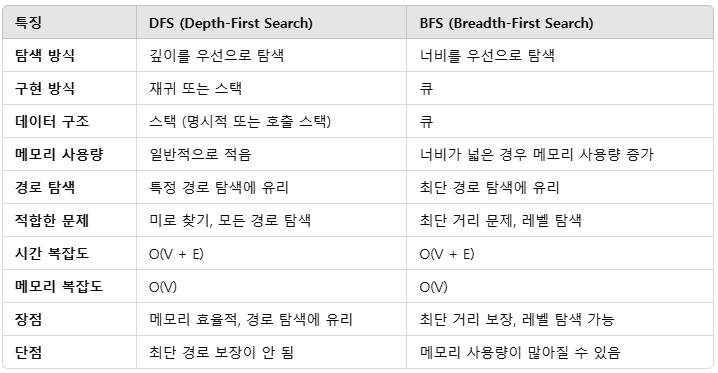
탐색 순서 또한 다르다. 아래 트리를 DFS와 BFS로 탐색해보자.

DFS에서는 탐색이 가능한 노드를 우선적으로 끝까지 탐색한다. 따라서 그래프 또는 트리 구성에 따라서 다르겠지만 왼쪽 하위 노드를 향해 탐색한다고 가정한다면 다음과 같다.
1 → 2 → 4 → 5 → 3 → 6 → 7
BFS에서는 현재 노드에서 탐색이 가능한 모든 노드를 탐색한 후 다음 깊이로 탐색을 이어나간다는 특징이 있다. 따라서 다음과 같은 탐색 순서를 가진다.
1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 5 → 6 → 7
한 가지 주의해야 할 점은 BFS로는 해결 가능한 문제가 문제의 제한 시간 등의 이유로 DFS로는 해결하지 못하거나 추가적인 처리가 필요한 경우가 존재한다. 가령 다음 입력에서 1의 개수를 출력한다고 가정해보자.
1 0 0
1 1 1
0 1 0
이때 (0, 0) 에서 DFS로 탐색을 한다고 가정하면 (2, 1) 또는 (1, 2)를 방문하지 않아 4가 출력될 수 있다. 하지만 BFS로 탐색을 하면 현재 위치 또는 노드에서 자신이 방문할 수 있는 모든 노드를 탐색하므로 그럴 일이 없다.
DFS와 BFS는 그래프 탐색의 기본적인 알고리즘으로, 다양한 심화 알고리즘을 이해하는 데 중요한 기초가 된다. 이 두 알고리즘을 잘 이해하면, 트리나 그래프와 관련된 더 복잡한 문제들을 해결할 때 그 기반을 활용할 수 있다.
예를 들어, DFS는 백트래킹이나 최단 경로 탐색 등의 문제에서 자주 사용되고, BFS는 최단 경로 문제(단방향 그래프에서)나 네트워크 흐름 문제 등에서 중요한 역할을 한다. 또한, DFS와 BFS는 알고리즘의 복잡도를 분석하는 데에도 중요한 기초가 되므로 잘 숙지해두면 좋다.
댓글남기기